differences between fatigue and torsion test|exhaustion testing methods : wholesaler Some common forms of test specimens and loading situations are shown in Fig 5.1. Note that test specimens are nothing more than specialized engineering components in which a known . WEBExplore @iamkaylanicole Instagram profile with posts and stories - Picuki.com. Picuki. Paste Trending. @iamkaylanicole Kayla Nicole └A . Stories. Tagged 662 Posts 652,568 .
{plog:ftitle_list}
web1 de ago. de 2023 · Check out one of the top 11 hot yoga studios in Toronto today! Whether you prefer relaxing restorative classes or intense sessions that test your limits, there’s .
types of fatigue testing
Torsion testing predicts a material’s behavior under twisting forces by assessing key properties such as torsional strength, shear modulus, yield strength in torsion, ductility, and brittleness. It enables the understanding of fatigue behavior, .What is the difference between creep test and fatigue test? Creep testing measures how a material deforms under constant load over time, while fatigue testing examines how it responds to repeated cyclic loading.
Some common forms of test specimens and loading situations are shown in Fig 5.1. Note that test specimens are nothing more than specialized engineering components in which a known .
audi a4 1.8t compression test
Torsion testing serves the purpose of scrutinizing how a material responds to twisting forces, elucidating its shear modulus, shear strength, torsional yield strength, and .The manufacturing process (CM wire) seems to play a major role in the superior fatigue resistance of the HYF files. In this study, there was no difference between HYF and GEN, .Torsion tests can be performed by applying only a rotational motion or by applying both axial (tension or compression) and torsional forces. Types of torsion testing vary from product to product but can usually be classified as .There are four scenarios we have discussed for analyzing fatigue: Fully reversed simple loading (i.e., mean zero) Fluctuating simple loading. Combined simple loading. Complex loading.
The S-N map provides unique insights to early detection of RCF driven fatigue damage. The S-N map was utilized to generate the surface damage S-N curve. Torsional .The purpose of a torsion test is to determine sample behaviour when twisted, or under torsional forces, as a result of applied moments that cause shear stress about the axis. Measurable values include: the modulus of elasticity in shear, .
The test sample is placed between compression test platens until the cellular structure fails or ruptures. A universal test machine can perform either or both tension and compression tests. The crosshead can be used to pull or compress the test sample which is located between the baseplate and the moving head. Dynamic & Fatigue Test Machines; Torsion Test Machines; Axial Torsion Test Machines; Planar Biaxial Test Machines; Single Purpose Test Machines; Test Machine Upgrades; . A major difference between the two types of machines is that the load and displacement performance of a servohydraulic actuator (depending on power pack size), can .
Torsion tests can be performed by applying only a rotational motion or by applying both axial (tension or compression) and torsional forces. Types of torsion testing vary from product to product but can usually be classified as . Torsion only: Applying only torsional load to the material; Axial-torsion Applying axial (tension/compression) and torsional force to a material. Failure testing: Twisting the product or material until it breaks or there is a visible defect. Proof testing Applying a torsional load to the material and holding the torque for a certain time.The torque to fracture and TtF were recorded. All the instruments underwent a SEM analysis. The heat-treated instruments showed a significantly higher fatigue resistance than the non-heat-treated instruments (p < 0.05). No significant differences were found in the torsional resistance between the ET and PTU, and the ETP and PTG. Note the following conversion factors between SI and English units: \(1 \mathrm{bar} \equiv 10^{5} \mathrm{Pa}, \quad 1 \mathrm{psi} \equiv 6.9 \times 10^{-2} \mathrm{bar}\), and \(1 \mathrm{bar}=14.5 \mathrm{psi}\) In Table 26.1, Young’s Modulus is tabulated for various materials. Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\) shows a plot of the stress-strain .
Statics - Twisting Moments. Twisting moments, or torques, are forces acting through distances (“lever arms”) so as to pro- mote rotation. The simple example is that of using a wrench to tighten a nut on a bolt as shown in Figure 6: if the bolt, wrench, and force are all perpendicular to one another, the moment is just the force F times the length l of the wrench: \(T = F \cdot l\).Stress related to shear is torsional stress. If we hold one end of our cylinder fixed and twist the other end as shown in the figure below, we are applying a torsional (or twisting) stress. Torsional Stress. Credit: Callister ‹ Reading Assignment up Examples of Materials Under Stress .
Testicular torsion is a painful condition of the testicle due to twisting the spermatic cord that causes loss of blood to the testicle. This a surgical emergency, as torsion is the most common cause of testicle loss in adolescent males. Testicle infection (also termed testicular infection and/or orchitis) generally means infection of the testicles by various bacteria and/or .
where σ a is the bending stress amplitude (for torsion accordingly τ a), N is the number of cycles until failure, and A and B are the parameters of the regression equation. The parameters in Equations (3), (14) and (15) were determined based on fatigue test data from Pawliczek and Rozumek [27,29].
The test conditions between the developed testing machine and conventional servohydraulic testing machine, i.e., the difference in waveforms, showed differences with regard to bending torsion and push–pull torsion, as well as test frequency. The definition of “failure life” was also different, as mentioned earlier.Statistical analysis showed statistically signiicant difference between Proile Vortex M Wire iles and the other instruments tested (P<0.05) in terms of the maximum rotation to fracture (degrees and turns). No signiicant difference was observed .Garud ~ (J. Test. Evaluations 1981, 9, 165) reviewed the results of multiaxial fatigue researches proposed . torsional fatigue strength for a given fatigue life, respectively, /3 is a material constant, and ~ is the . is the phase difference between bending and torsion. Lee and Chiang 9 modified Equation (3) into the follow- ing Equation (4 .Understanding the differences between torque and torsion is crucial for engineers, physicists, and anyone working with rotating systems or materials subjected to twisting forces. Comparisons may contain inaccurate information about people, places, or .
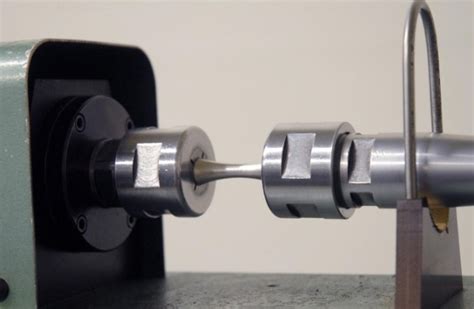
Torsion testing involves the twisting of a sample along an axis and is a useful test for acquiring information like torsional shear stress, maximum torque, shear modulus, and breaking angle of a material or the . TestResources manufactures and supplies universal test machines, tensile testers, dynamic testing machines, and much more. Call us today (800)430-6536. The torsional test was performed on a tensile torsion electromechanical single-column device (Model 5944; Instron, Norwood, MA), which permitted the conduction of a torsion test according to ISO 3630-1 .
Torsion fatigue experiments were conducted using MTS torsional fatigue test rig. The details of this test rig are provided by Bomidi et al. [48]. Fully reversed torsion fatigue tests were conducted using torque control technique. The torque amplitudes selected for fatigue testing were in the range of 0.3S us to 0.7S us. A frequency of 40 Hz was .(i.e. reduced gage section). Fatigue tests revealed that the specimens subjected to the axial loading exhibited lower fatigue resistance compared to the specimens failed under rotating bending test. Such differences in the fatigue life was attributed to the variation in the stress distribution resulting
This teaching and learning package provides an introduction to the mechanics of beam bending and torsion, looking particularly at the bending of cantilever and free-standing beams and the torsion of . Yield Strength vs Tensile Strength Tensile strength quantifies the force needed to pull a rope, wire, or a structural beam to the stage where it breaks. Specifically, the tensile strength of a material is the
multiaxial excitation [4]. The difference in fatigue failure was proven experimentally in [5], performing end of life tests with a statistically sufficient number of test specimens in the form of quadratic rods with rectangular notches. The investigation showed differences in fatigue life between sequential uniaxial and multiaxial excitation.Most fatigue testing is conducted at the basic material level; differences between laboratory and service conditions must be considered by mechanical designers. Common test specimen types for obtaining fatigue data are shown in Figure 6. Figure 6 Fatigue Test Specimens: (a) Rotating Bending, (b) Cantilever Flat Sheet (cont.)
An attempt has been made to examine any differences in behavior between uni-axial fatigue and repeated torsion fatigue. In order to eliminate the stress gradient effect, thin-walled hollow cylindrical specimens were used. Low cycle fatigue tests of mild steel were conducted in uni-axial and torsional loading at constant strain amplitude.
Higher carbon 1060 steel can be completely transformed to austenite at 850, a 100 °C lower temperature than that for conventionally used 1045 steel, allowing development of very small austenite grains during induction hardening. Torsion fatigue test specimens were machined from quenched and tempered martensite and as hot-rolled pearlitic bars of 1060 . They found no significant difference between the two specimens fatigue lives for low strain amplitudes, while the difference in fatigue life increased when strain amplitude was larger. Combined axial-torsion fatigue tests on several tubular specimens were conducted in [8] to study the thickness effect of the gage section.Testing Metals: Is it Creep Failure or Fatigue. Creep failure and fatigue in metals are both time-dependent issues that can have a devastating effect on metallic components – but they aren’t the same thing. Discover the difference between these two common metal deformation faults and find out more about how they can affect the integrity of your metal parts and components.

audi a4 b6 compression test
WEB28 de jul. de 2022 · https://fapello.com/anitta/ https://fapello.com/mc-mirella/ https://fapello.com/vanessa-vailatti/ https://fapello.com/juliana-bonde/ .
differences between fatigue and torsion test|exhaustion testing methods